Hip Osteoarthritis
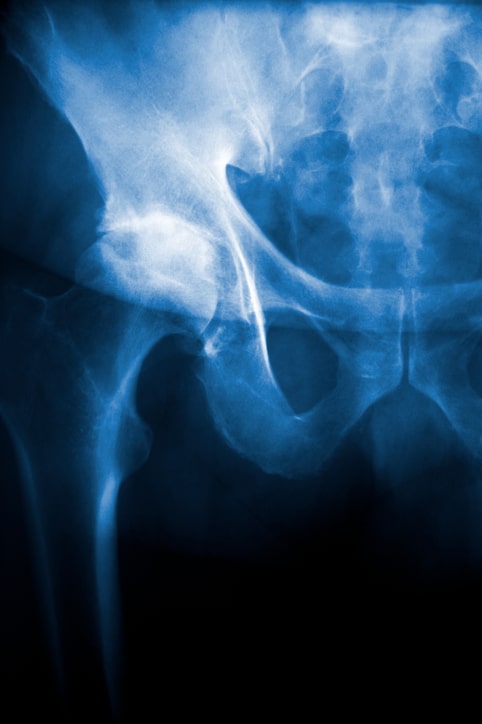
Osteoarthritis of the hip is a common condition resulting in groin or hip pain due to wear and tear of cartilage or degenerative changes to the hip joint.
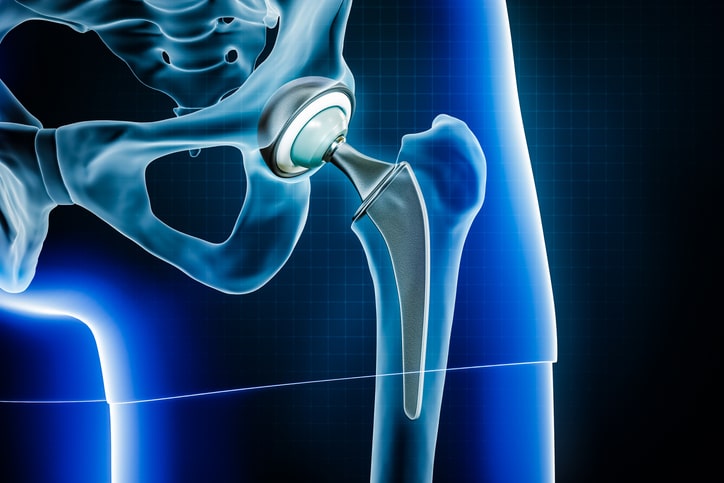
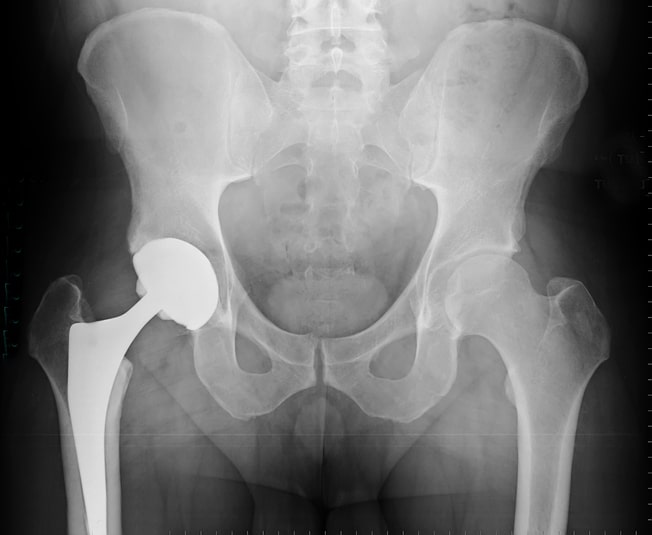
Hip osteoarthritis is typically age related and often presents in patients over 50 years old. However, osteoarthritis can also be seen in younger patients. The severity can range from mild to severe bone on bone arthritis. Signs and symptoms include pain to the groin, radiating pain to thigh or knee, stiffness, locking or catching at the hip, and difficulty performing daily activities such as walking, bending forward to tie a shoe, or standing from seated position. X-rays are typically used for diagnosis. Initial, nonoperative management include activity modification, physiotherapy, topical or oral anti-inflammatories, pain medication, and assisted devices such as a walker or cane. Steroid injections or nerve ablations may also be considered for nonoperative management. If nonoperative management fails or if condition is severe, surgery may be indicated. In general, a total hip replacement is the surgical option for severe hip osteoarthritis.